Tips for solar charging your data collection
Post by Julia Connors of Voltaicsystems. Email Julia with questions: julia@voltaicsystems.com
What is solar for M&E?
Solar technology can be extremely useful for M&E projects in areas with minimal or inconsistent access to power. Portable solar chargers can eliminate power constraints and keep phones and tablets reliably charged up in the field.
In this post we’ll discuss:
- How to decide if solar is right for your project
- How to properly size a solar charging system to meet your needs
Do you really need solar?
In many cases solar is not necessary and will simply add complexity and costs to your project. If your team can return every day to a central location with access to power, then the battery power of the tablet is sufficient in most scenarios. If not, we recommend implementing standard power saving tips to reduce power consumption during time out collecting data.
POWER SAVING TIPS
If you do have daily access to the grid but find that users need to recharge at least once while out or need to spend more than one day without power, then add an external battery pack. This cost-effective option allows your team to have extra power without carrying a full solar charging system. To size a battery for your needs, skip down to ‘Step 3’ below.
If you don’t have reliable access to grid power, the next section will help you determine which size solar charging system is best for you.
Sizing your solar charger system
The key to making solar successful in your project is finding the best system for your needs. If a system is underpowered then your team can still run out of power when they’re collecting data. On the other hand, if your system is too powerful it will be heavier and more expensive than needed. We recommend the following three steps for sizing your solar needs:
- Estimate your daily power consumption
- Determine your minimum solar panel size
- Determine your minimum battery size
Step 1: Estimate your daily power consumption
Once you have chosen the device you will be using in the field, it’s easy to determine your daily power consumption. First you’ll need to figure out the size of your device’s battery (in Watt hours). This can often be found by looking on the back of the battery itself or doing a quick Google search to find your device’s technical specifications.
Next, you’ll need to determine your battery usage per day. For example, if you use half of your device’s battery on a typical day of data collection, then your usage is 50%. If you need to recharge twice in one day, then your usage is 200%.
Once you have those numbers, use the formula below to find your daily power consumption:
Size of Device’s Battery (Wh) x Battery Usage (per day) =
Daily Power Consumption (Wh/day)
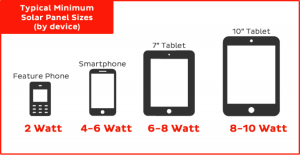
Step 2: Determine your minimum solar panel size
The larger your device, the bigger the solar panel (measured in Watts) you’ll need. This is because larger solar panels can generate more power from the sun than smaller panels. To determine the best solar panel size for your needs, use our formula below:
Daily Power Consumption (from Step 1) / Expected Hours of Good Sun*
x 2 (Standard Power Loss Variable) =
Solar Panel Minimum (Watts)
*We typically use 5 hours as a baseline for good sun and then adjust up or down depending on the conditions. High temperatures, clouds, or shading will reduce the power produced by the panel.
Since solar conditions change frequently throughout the day, we recommend choosing a panel that is 2-4 times the minimum size required.
Step 3: Determine minimum battery size
External batteries offer extra power storage so that your device will be charged when you need it. The battery acts as a perfect backup on cloudy and rainy days so it’s important to choose the right size for your device.
It can vary, but typically about 30% of power is lost in the transfer from the external battery to your device. Therefore, to determine the battery capacity needed for one day of use, we’ll use our power consumption data from Step 1 and divide by 0.7 (100% – 30% power loss).
Watt hours per day / 0.7 hours =
Watt battery capacity needed for 1 day of use

Picking the right system for your project
Now that you’ve done the math, you’re one step closer to choosing a solar charging system for your project. Since solar chargers come in many different forms, the last step to determining your perfect system is to think about how your team will be using the solar chargers in their work. It’s important to factor in storage for device/cables and how the user will be carrying the system.
Most users aren’t that technical, so having a pack that stores the battery and the device can simplify their experience (rather than handing over a battery and a panel that they need to figure how to organize during their day). By simply finding the right style and size, you’ll experience higher usage rates and make your team’s solar-powered data collection go more smoothly.
You might also like
-
Hands on with GenAI: predictions and observations from The MERL Tech Initiative and Oxford Policy Management’s ICT4D Training Day
-
When Might We Use AI for Evaluation Purposes? A discussion with New Directions for Evaluation (NDE) authors
-
A visual guide to today’s GenAI landscape
-
Register now for the NLP-CoP Ethics and Governance Working Group Meeting on April 18th